ReactJS - Conditional Rendering
Conditional Rendering in React refers to rendering UI elements based on certain conditions. It allows developers to control what is displayed to the user based on the current state of the application, user interactions, or data. Conditional rendering in React works similarly to how conditions are used in standard JavaScript. You can use JavaScript operators and control flow statements within your JSX to determine which elements or components should be rendered.
Using if-else Statement:
In React, the if-else statement is a fundamental way to render different components or JSX based on a condition. It's useful when your rendering logic is complex or when you're choosing between two different render paths.
const UserList = (props) => {
const isLoggedIn = props.isLoggedIn;
if (isLoggedIn) {
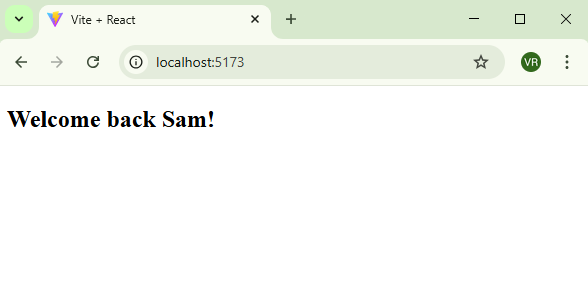
return <h2>Welcome back {props.name}!</h2>;
} else {
return <h2>Please Login.</h2>;
}
};
export default UserList;
import UserList from './components/UserList'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<UserList isLoggedIn={true} name={'Sam'} />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
In this example:
- React checks the isLoggedIn value.
- If it's true, it returns one JSX block.
- If it's false, it returns another.
Output:
Using Ternary Operator:
The ternary operator is a concise way to conditionally render elements in React within JSX. It works like a simple if-else , but inline.
Syntax:
condition ? expressionIfTrue : expressionIfFalse
const UserList = (props) => {
const isLoggedIn = props.isLoggedIn;
return (
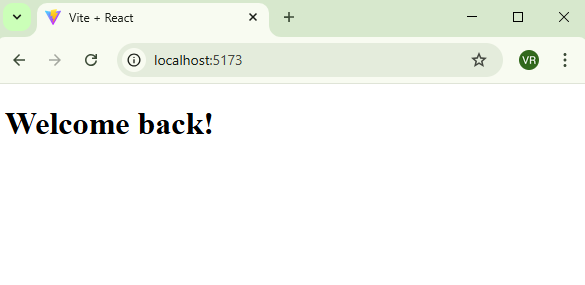
<div>{isLoggedIn ? <h1>Welcome back!</h1> : <h1>Please log in.</h1>}</div>
);
};
export default UserList;
import UserList from './components/UserList'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<UserList isLoggedIn={true} />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Output:
Using Logical AND (&&):
The Logical AND (&&) operator is a simple and elegant way to render something only when a condition is true — no else part.
Syntax:
condition && expressionIfTrue
function UserList({ notification }) {
return (
<div>
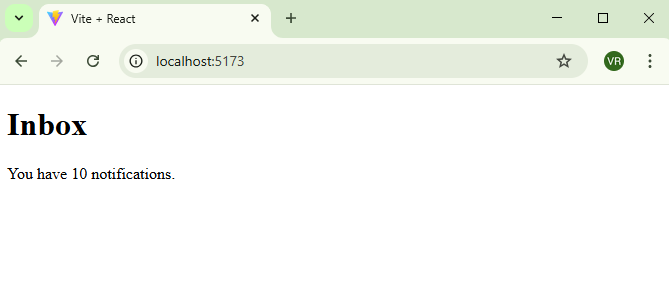
<h1>Inbox</h1>
{notification > 0 && <p>You have {notification} notifications.</p>}
</div>
);
}
export default UserList;
import UserList from './components/UserList'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<UserList notification ={10} />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Output:
Using switch Statement:
The switch statement is a clean and readable way to handle multiple rendering conditions — especially when there are more than two possible states.
function UserList({ status }) {
switch (status) {
case 'loading':
return <p>Loading...</p>;
case 'success':
return <p>Data loaded successfully!</p>;
case 'error':
return <p>Failed to load data.</p>;
default:
return <p>Idle...</p>;
}
}
export default UserList;
import UserList from './components/UserList'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<UserList status ={'success'} />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Output:
Use Rendering null (Render Nothing):
In React, sometimes you may want to render nothing — not even an empty <div> based on a condition. Instead of showing a component or HTML element, you simply return null from the component’s render method or function body.
function Welcome({ isLoggedIn }) {
if (!isLoggedIn) {
return null; // Render nothing if not logged in
}
return <h2>Welcome back, User!</h2>;
}
function App() {
const isLoggedIn = false; // Change this to true to show the message
return (
<div>
<h1>My Application</h1>
<Welcome isLoggedIn={isLoggedIn} />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Output: