Django Models
What is Django Models
- Django models are a powerful way to interact with your database in a structured and organized manner.
- Each model class typically represents a database table, with its attributes defining the fields of the table.
- In Django, data is represented using objects called models, which correspond to tables in a database.
Using MySQL with Django
- MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) widely used in web applications due to its performance, reliability, and scalability.
- Django supports MySQL as a database backend, allowing you to store and manage your application's data.
1. Install MySQL Client for Python
To use MySQL with Django, you need to install the mysqlclient package.
pip install mysqlclient
2 Configure MySQL in settings.py
In your Django project's settings.py, update the DATABASES section like this:
DATABASES = { 'default': { 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql', 'NAME': 'db_ecommerce', 'USER': 'root', 'PASSWORD': '', 'HOST':'localhost', 'PORT':'3306', } }
3. Creating a Django Model
After setting up MySQL, you need to create a model inside your myproject/myapp/models.py file.
Example: Defining a Product Model
from django.db import models class Product(models.Model): product_name = models.CharField(max_length=150) price = models.FloatField() unit = models.CharField(max_length=20) class Meta: db_table = "tbl_products"
4. Make Migrations
Run python manage.py makemigrations
Django creates a migration file that describes the changes made to your models and stores the file in the /migrations/ folder
python manage.py makemigrations myapp
D:\django_projects\myproject>python manage.py makemigrations myapp Migrations for 'myapp': myapp\migrations\0001_initial.py - Create model Product
4. Migrate
The migrate command applies the migration files to your actual database( executing the database operations described in your migration files).
python manage.py migrate
D:\django_projects\myproject>python manage.py migrate Operations to perform: Apply all migrations: admin, auth, contenttypes, myapp, sessions Running migrations: Applying contenttypes.0001_initial... OK Applying auth.0001_initial... OK Applying admin.0001_initial... OK Applying admin.0002_logentry_remove_auto_add... OK Applying admin.0003_logentry_add_action_flag_choices... OK Applying contenttypes.0002_remove_content_type_name... OK Applying auth.0002_alter_permission_name_max_length... OK Applying auth.0003_alter_user_email_max_length... OK Applying auth.0004_alter_user_username_opts... OK Applying auth.0005_alter_user_last_login_null... OK Applying auth.0006_require_contenttypes_0002... OK Applying auth.0007_alter_validators_add_error_messages... OK Applying auth.0008_alter_user_username_max_length... OK Applying auth.0009_alter_user_last_name_max_length... OK Applying auth.0010_alter_group_name_max_length... OK Applying auth.0011_update_proxy_permissions... OK Applying auth.0012_alter_user_first_name_max_length... OK Applying myapp.0001_initial... OK Applying sessions.0001_initial... OK
After migration the database will look like this:
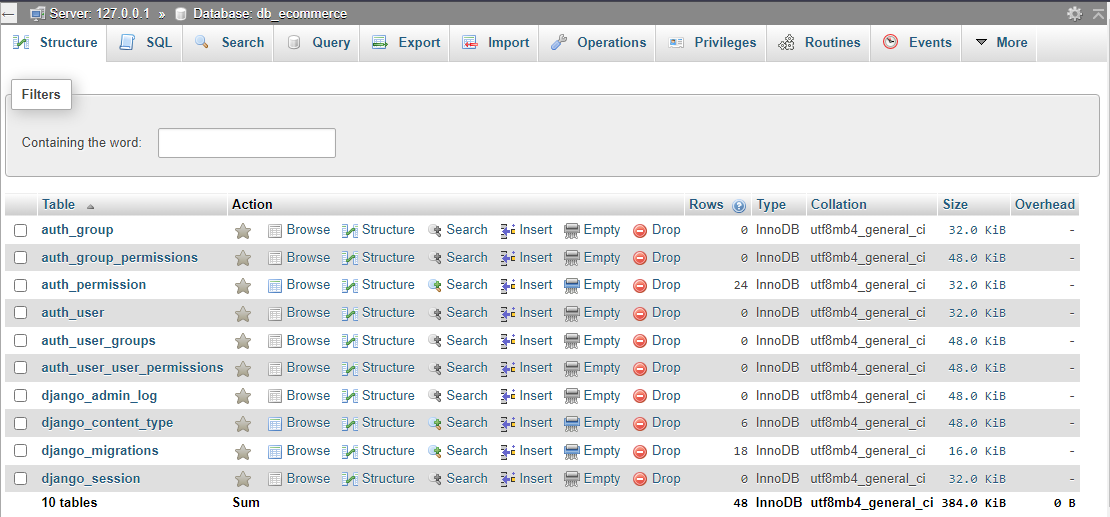
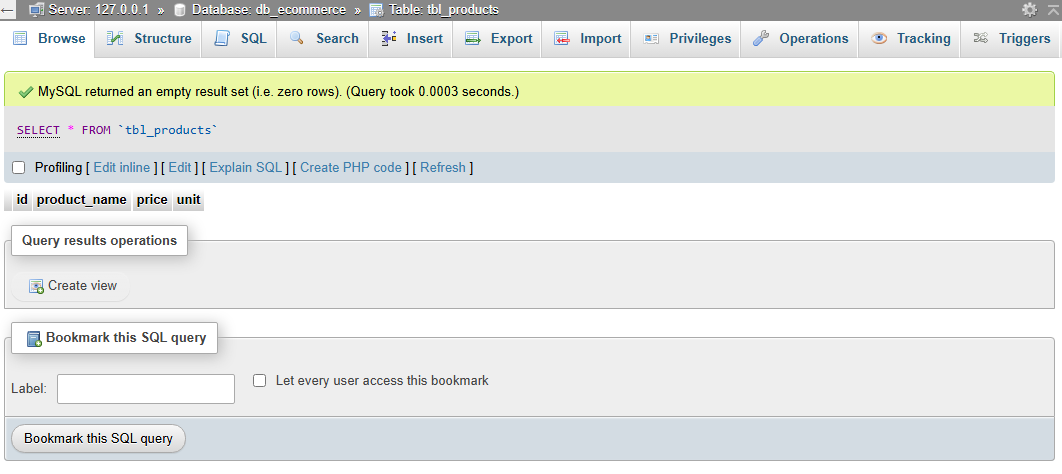
Common Field Types
| Field Type | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
AutoField |
Integer that auto-increments; primary key by default. | id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) |
CharField |
Short text (needs max_length) |
name = models.CharField(max_length=100) |
TextField |
Long text | description = models.TextField() |
IntegerField |
Integer values | quantity = models.IntegerField() |
DecimalField |
Decimal numbers (need max_digits, decimal_places) |
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2) |
BooleanField |
True/False | is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True) |
DateTimeField |
Date and time (auto_now_add for creation) |
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True) |
DateField |
Only date | birth_date = models.DateField() |
ForeignKey |
One-to-many relation | category = models.ForeignKey(Category, on_delete=models.CASCADE) |
ManyToManyField |
Many-to-many relation | tags = models.ManyToManyField(Tag) |
OneToOneField |
One-to-one relation | profile = models.OneToOneField(Profile, on_delete=models.CASCADE) |
ImageField |
Image upload (needs Pillow) | photo = models.ImageField(upload_to='images/') |
FileField |
File upload | document = models.FileField(upload_to='docs/') |
BigAutoField |
64-bit integer that auto-increments; primary key alternative to AutoField. | id = models.BigAutoField(primary_key=True) |
BigIntegerField |
Large integers (64-bit). | views = models.BigIntegerField() |
SmallIntegerField |
Small range of integer values. | rating = models.SmallIntegerField() |
PositiveIntegerField |
Positive integers only (>= 0). | stock = models.PositiveIntegerField() |
PositiveSmallIntegerField |
Small positive integers (>= 0). | rank = models.PositiveSmallIntegerField() |
FloatField |
Floating-point numbers. | rating = models.FloatField() |
EmailField |
CharField that checks for valid email format. | email = models.EmailField() |
URLField |
Validates URLs; rendered as a URL input in forms. | website = models.URLField() |
SlugField |
Short label for URLs, typically generated from another field (e.g. title). | slug = models.SlugField(unique=True) |
UUIDField |
Stores a universally unique identifier (UUID). | uid = models.UUIDField(default=uuid.uuid4, editable=False, unique=True) |
GenericIPAddressField |
Stores IPv4 or IPv6 addresses. | ip_address = models.GenericIPAddressField() |
TimeField |
Stores only time values (no date). | start_time = models.TimeField() |
DurationField |
Stores Python timedelta values (e.g., for time intervals). |
duration = models.DurationField() |
BinaryField |
Stores raw binary data (e.g., for files or binary blobs). | filedata = models.BinaryField() |
JSONField |
Stores structured JSON data (Django 3.1+). | metadata = models.JSONField() |