Django Cookies
What Are Cookies?
Cookies are small pieces of data stored by a web browser on the user's computer. They are used to remember information about the user or their activity on a website. When a user visits a website, the website can send cookies to the user's browser, which the browser stores locally. The next time the user visits the website, the browser sends the cookies back to the website, allowing the site to remember the user’s previous actions or settings.
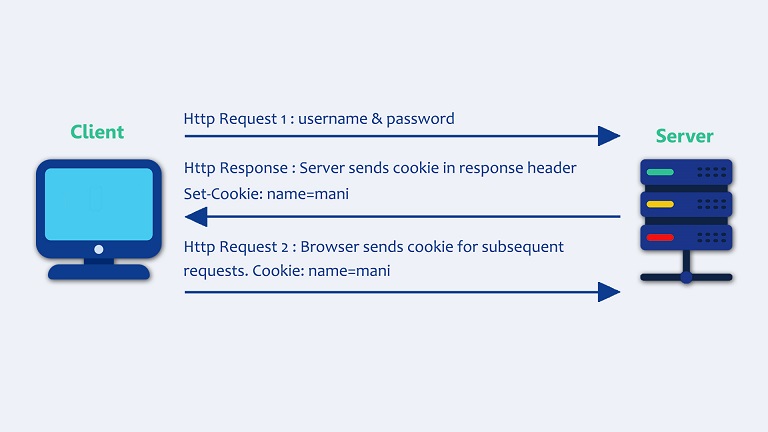
Why We Use Cookies?
- Session Management: Cookies are often used to manage user sessions. For example, after a user logs into a website, a cookie can store their session data to keep them logged in as they navigate between pages.
- Personalization: Cookies can store user preferences, like language settings or theme preferences, so that when they return to the website, it can offer a more personalized experience.
- Tracking and Analytics: Cookies are used to track user behavior on websites (like which pages they visit or how long they stay on a page). This helps website owners understand user preferences and improve the site.
- Shopping Carts: Cookies are used to remember items added to a shopping cart in e-commerce sites. This way, even if the user leaves the site and returns later, the cart is still filled with the items they added previously.
- Advertising: Cookies are used for targeted advertising. By tracking the pages a user visits, cookies can help serve ads that are more relevant to the user.
File and Folder Structure
1. Create the Views
myapp/views.pyThis code defines views to set, get, and delete a cookie with the username. The set_cookie view stores the username, get_cookie displays it, and delete_cookie removes the cookie.
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect def set_cookie(request): if request.method == 'POST': username = request.POST.get('username') response = redirect('get_cookie') response.set_cookie('username', username, max_age=60*60*24) # 1 day return response return render(request, 'set_cookie.html') def get_cookie(request): username = request.COOKIES.get('username', 'Guest') return render(request, 'get_cookie.html', {'username': username}) def delete_cookie(request): response = redirect('get_cookie') response.delete_cookie('username') return response
2. Create Templates
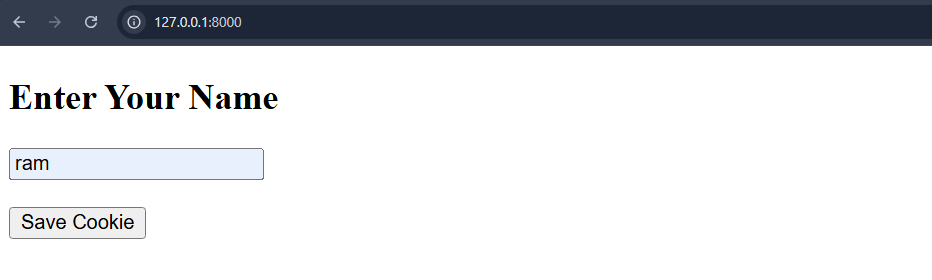
myapp/templates/set_cookie.htmlThis page allows the user to enter their name and save it as a cookie. The form submits the username, which is then stored for future visits.
<html> <head> <title>Set Cookie</title> </head> <body> <h2>Enter Your Name</h2> <form method="post"> {% csrf_token %} <input type="text" name="username" required><br><br> <input type="submit" value="Save Cookie"> </form> </body> </html>myapp/templates/get_cookie.html
This page displays a welcome message with the username stored in the cookie. It also provides a link to delete the cookie, allowing the user to log out.
<html> <head> <title>Get Cookie</title> </head> <body> <h2>Welcome, {{ username }}!</h2> <p><a href="{% url 'delete_cookie' %}">Delete Cookie</a></p> </body> </html>
This code defines URL patterns for handling cookie operations in Django. It includes paths for setting a cookie, retrieving it, and deleting it.
from django.urls import path from . import views urlpatterns = [ path('', views.set_cookie, name='set_cookie'), path('get/', views.get_cookie, name='get_cookie'), path('delete/', views.delete_cookie, name='delete_cookie'), ]
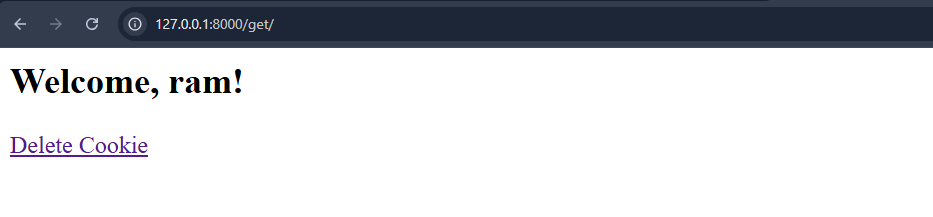
Output
Set Cookie Page
This page allows users to enter their name and set a cookie with their username. The cookie is stored for one day and will be used for subsequent visits.
Show Cookie Page
This page displays the username stored in the cookie. If the cookie is not found, a message indicating that the cookie has been deleted will be shown instead.